티스토리 뷰
프록시 팩토리
스프링은 유사한 구체적인 기술들이 있을 때, 그것들을 통합해서 일관성 있게 접근할 수 있고 편리하게 사용할 수 있도록 추상화된 기술을 제공한다. 동적 프록시를 통합해서 프록시 팩토리라는 기능을 제공하는데, 프록시 팩토리는 인터페이스가 있으면 JDK 프록시를 사용하고, 구체 클래스가 있다면 CGLIB를 사용한다. 이 내용은 설정을 통해 변경할 수도 있다.
Advice
Advice는 프록시에 적용하는 부가 기능 로직이다.
JDK 동적 프록시가 제공하는 InvocationHandler와 CGLIB가 제공하는 MethodInterceptor의 개념과 유사한데, 이 둘을 추상화 한 것이다. 프록시 팩토리를 사용한다면 이 둘 대신에 Advice를 사용하면 된다.
Advice를 만드는 방법은 다양하지만, MethodInterceptor를 구현해서 만들어보자.
package org.aopalliance.intercept;
public interface MethodInterceptor extends Interceptor {
Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable;
}MethodInvocation invocation: 내부에는 다음 메서드를 호출하는 방법, 현재 프록시 객체 인스턴스, args , 메서드 정보 등이 포함되어 있다.MethodInterceptor는Interceptor를 상속하고,Interceptor는Advice인터페이스를 상속한다.
Advice - 인터페이스가 있다면, JDK 동적 프록시 사용
TimeAdvice.class
@Slf4j
public class TimeAdvice implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
log.info("TimeProxy 실행");
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Object result = invocation.proceed();
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
long resultTime = endTime - startTime;
log.info("resultTime={}", resultTime);
return result;
}
}TimeAdvice는MethodInterceptor인터페이스를 구현한다.invocation.proceed()를 호출하면target클래스를 호출하고 그 결과를 받는다.
ServiceInface.interface
public interface ServiceInterface {
void save();
void find();
}Test code
@Slf4j
public class ProxyFactoryTest {
@Test
@DisplayName("인터페이스가 있으면 JDK 동적 프록시 사용")
void interfaceProxy() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target); // 프록시를 생성할 때, target 클래스를 넘겨준다.
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
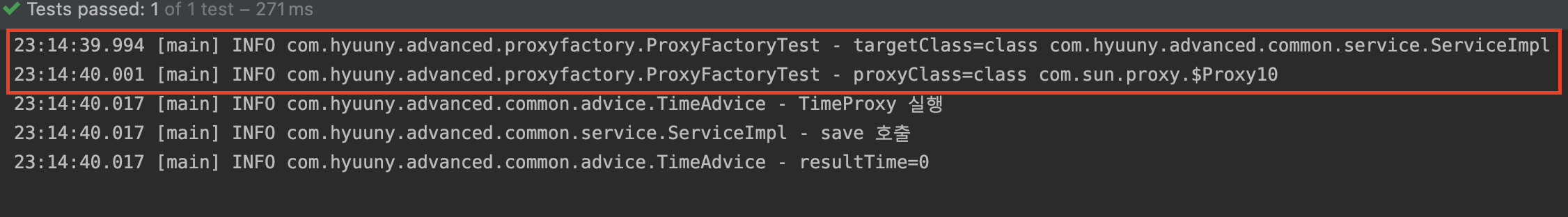
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass()); // targetClass=class com.hyuuny.advanced.common.service.ServiceImpl
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass()); // proxyClass=class com.sun.proxy.$Proxy10
proxy.save();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue(); // 프록시라면 True
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isTrue(); // JDK 동적 프록시라면 True
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isFalse(); // CGLIB 동적 프록시라면 True
}
}new ProxyFactory(target): 프록시 팩토리를 생성할 때, 생성자에 프록시의 호출 대상을 함께 넘겨준다. 만약 이 인스턴스에 인터페이스가 있다면 JDK 동적 프록시를 기본으로 사용하고, 인터페이스 없이 구체 클래스만 있다면 CGLIB를 통해서 동적 프록시를 생성한다. 위 코드에서는ServiceInterface인터페이스가 존재하기때문에, JDK 동적 프록시를 생성한다.proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice()): 프록시 팩토리를 통해서 만든 프록시의 부가 기능 로직을 설정한다. JDK 동적 프록시가 제공하는InvocationHandler와 CGLIB가 제공하는MethodInterceptor의 개념과 유사하다.proxyFactory.getProxy(): 프록시 객체를 생성하고 그 결과를 받는다.
결과
Advice - 구체 클래스만 있다면, CGLIB 프록시 사용
ConcreteService.class
@Slf4j
public class ConcreteService {
public void call() {
log.info("ConcreteService 호출");
}
}Test code
@Test
@DisplayName("구체 클래스만 있으면 CGLIB 사용")
void concreteProxy() {
ConcreteService target = new ConcreteService();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target); // 프록시를 생성할 때, target 클래스를 넘겨준다.
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ConcreteService proxy = (ConcreteService) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass());
proxy.call();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isFalse(); // JDK 동적 프록시라면 True
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isTrue(); // CGLIB 동적 프록시라면 True
}결과
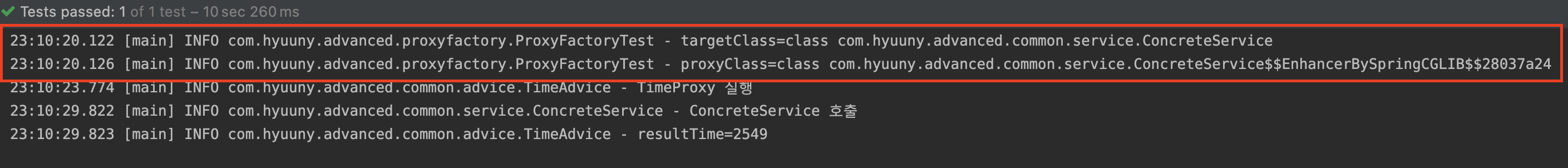
com.hyuuny.advanced.common.service.ConcreteService$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$28037a24 코드를 통해 CGLIB 프록시가 적용된 것도 확인할 수 있다
Advice - 옵션을 사용하면 인터페이스가 있어도 CGLIB를 사용해서 클래스 기반 프록시 사용
Test code
@Test
@DisplayName("proxyTargetClass 옵션을 사용하면 인터페이스가 있어도 CGLIB를 사용해서, 클래스 기반 프록시 사용")
void proxyTargetClass() {
ServiceInterface target = new ServiceImpl();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory(target); // 프록시를 생성할 때, target 클래스를 넘겨준다.
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true); // setProxyTargetClass를 true로 주면 인터페이스가 있어도 CGLIB를 기반으로 사용
proxyFactory.addAdvice(new TimeAdvice());
ServiceInterface proxy = (ServiceInterface) proxyFactory.getProxy();
log.info("targetClass={}", target.getClass());
log.info("proxyClass={}", proxy.getClass());
proxy.save();
assertThat(AopUtils.isAopProxy(proxy)).isTrue();
assertThat(AopUtils.isJdkDynamicProxy(proxy)).isFalse(); // JsetProxyTargetClass(true) 설정으로 False
assertThat(AopUtils.isCglibProxy(proxy)).isTrue(); // setProxyTargetClass(true) 설정으로 True
}결과
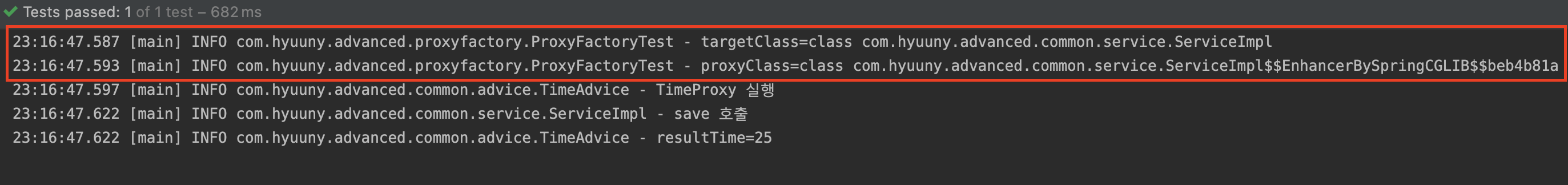
ServiceInterface라는 인터페이스가 있지만, proxyTargetClass 옵션을 통해 CGLIB 기반의 프록시가 생성된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
스프링 부트는 2.0 이후로 AOP를 적용할 때 기본적으로 proxyTargetClass=true로 설정해서 사용하기 때문에, 인터페이스가 있어도 항상 CGLIB를 사용해서 구체 클래스를 기반으로 프록시를 생성한다. 이에 대한 자세한 내용은 추후 포스팅할 계획이다.
Reference
김영한. 스프링 핵심 원리 - 고급편. 인프런.
https://www.inflearn.com/course/%EC%8A%A4%ED%94%84%EB%A7%81-%ED%95%B5%EC%8B%AC-%EC%9B%90%EB%A6%AC-%EA%B3%A0%EA%B8%89%ED%8E%B8#
'Spring' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Spring] 빈 후처리기(BeanPostProcessor) (0) | 2022.05.21 |
|---|---|
| [Spring] 포인트컷(Pointcut) (0) | 2022.05.19 |
| [Spring] 리플렉션(Reflection) (0) | 2022.05.15 |
| [Spring] ThreadLocal을 사용해보자! (0) | 2022.05.07 |
| [Spring] 트랜잭션 AICD (0) | 2022.04.20 |
- Total
- Today
- Yesterday
- Real MySQL
- 문자열
- 정렬
- 구현
- 북클럽
- 백준
- 자료구조
- 코테
- 코틀린
- 리팩토링
- leetcode
- 파이썬
- 노마드
- mysql 8.0
- 노마드코더
- Spring
- 김영한
- 그리디
- 릿코드
- 데이터베이스
- kotlin
- 인프런
- MySQL
- 알고리즘
- webflux
- spring boot
- 스프링
- 스프링 부트
- Algorithm
- 스프링부트
| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 |
| 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 |
| 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |

